Liposuction is the removal of fat from undesirable places on the body. It is one of the most common cosmetic procedures in the world. The goal of liposuction is to contour parts of the body in order to give it a natural, attractive appearance. It is commonly performed on the abdomen, thighs, back, arms, chest, buttocks, neck, and face. Liposuction is not a weight loss surgery and often requires a healthy lifestyle post-operatively to maintain the results. Although fat typically does not return to suctioned areas, it can deposit in other parts of the body. In this article, we tell you what everybody ought to know before taking the next step.
Who Performs Liposuction
Liposuction is one of the safer cosmetic surgery procedures when performed by a plastic surgeon trained in a plastic surgery residency accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
Plastic surgeons who have achieved board certification carry an additional badge that signals they have proven they have the training, skills, knowledge, and experience to deliver safe and expected outcomes for plastic surgery patients. All liposuction procedures should take place in accredited surgical facilities in order to ensure the environment the surgeon and their team are working in meets measurable standards for safety and care. All board certified plastic surgeons must operate in accredited surgical facilities. CLICK HERE to learn more about facility accreditation. CLICK HERE to learn more about board certification.
There are several liposuction techniques. Three of the main techniques used today are Suction Assisted Lipectomy (SAL), Ultrasound-Assisted Lipectomy (UAL), and Power Assisted Lipectomy (PAL). The most often used technique is SAL because of the lowered risk of complications and undesirable outcomes compared to UAL and PAL.
What is Liposuction Surgery
Before performing suction-assisted liposuction, plastic surgeons take a deep dive into the patient’s medical history. They also order laboratory tests and perform physical examinations to determine if the patient is a good candidate for plastic surgery. Once the surgeon determines the patient has met the criteria to move forward with liposuction, and the formalities of the consultation are complete, the following typically takes place:
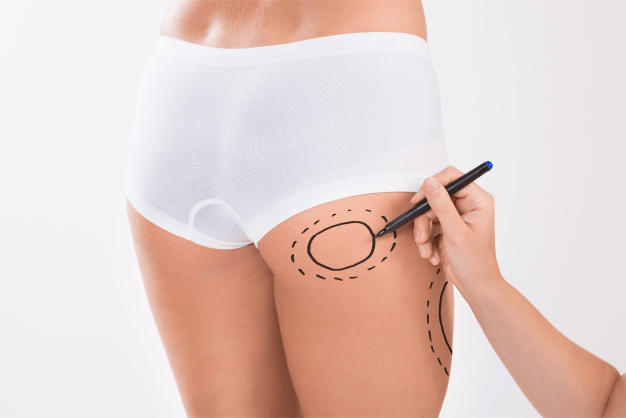
- The plastic surgeon takes photos of the patient’s body and points out scars, uneven and unbalanced areas, dimples and grooves, and cellulite already present.
- The surgeon places markings on the body to show suction targets (circles) and areas to avoid (hash marks). Incision marks are often in the creases of the skin to reduce visibility.

- A solution sometimes referred to as a tumescent or wetting solution, is injected into the areas where the suction will occur. It commonly consists of a lidocaine and epinephrine mixture. The lidocaine numbs the area and epinephrine reduces bleeding. Some plastic surgeons add sodium bicarbonate to reduce burning during the injection.
- There is an approximately 30-minute wait period to allow the surgery site to become numb.
- The patient is prepared and positioned for surgery.
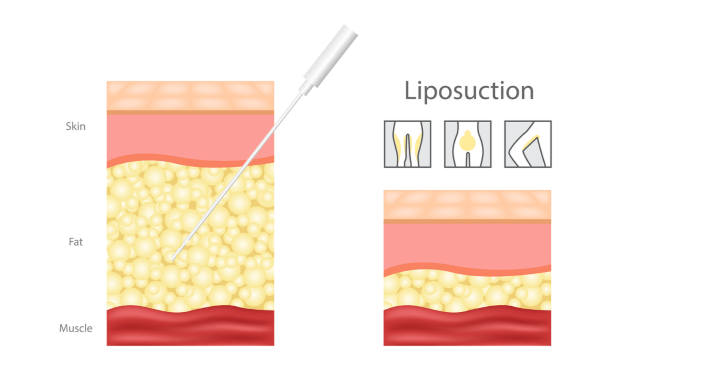
The plastic surgeon uses a spear-like instrument with tiny holes at and near the tip called a cannula for suctioning. The cannula slides into the incision site, and the surgeon’s non-dominant hand rests on the skin. The surgeon needs to feel the location of the cannula throughout the procedure to ensure proper placement. Then, fat suctioning using crisscross movements under the skin begins.
Where does the Fat from Liposuction Go
If the plastic surgeon intends to reinject the fat into another part of the body, it goes into a syringe for later use. Otherwise, the anesthesiologist or nurse anesthesiologist measures the amount of fat suctioned (up to 5 liters) to ensure the proper balance of fluid suctioned vs fluid that remains in the body. After the procedure, drain insertion into the incision sites allows draining of the tumescent or wetting fluid. It is important to allow the fluid to drain to reduce swelling from fluid retention.
Liposuction procedures generally last less than 3 hours. After surgery, plastic surgeons typically place compression wraps or garments on patients. Compression garments reduce swelling and maintain the body’s new contours. They also provide comfort and support until the body is completely healed.
Additionally, plastic surgeons often write prescriptions for pain medication, anti-nausea and vomiting medication, enoxaparin (anticoagulant), medication for muscle spasms, antifungal medication, and an antibiotic.
What to Expect After Liposuction
The most common after-effects of liposuction are swelling, numbness, bruising, and discoloration of the skin from bleeding. By the end of 3 months, the swelling, bruising, and discoloration of the skin usually resolve. Scarring is minimal because the incision sites are small and hidden in the folds and creases of the skin. However, genetics and the surgeon’s technique can make scarring more noticeable.
The less common, but more serious complications include seroma, hematoma, infection, fat embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. Body fat consists of fat cells, blood vessels, nerves, collagen, and cells that respond to injury in the body. Plastic surgeons performing liposuction are removing fat cells from this tissue. When there is damage to the nerves, blood vessels, or collagen framework in the suctioned area, complications can occur.
Who is a Candidate for Liposuction
The best candidates for liposuction are patients who want to enhance their body’s contours. They are:
- Within 30% of their ideal BMI
- Non-smokers
- Not diabetic or have a Hemoglobin A1C < 6.5%
- Normal liver and kidney function
- Not taking medications that interact with anesthesia
- Not taking medications that can cause blood clotting or bleeding
Plus, they have a past medical history that DOES NOT include deep vein thrombosis (DVT), Pulmonary embolism (PE). Additionally, they have controlled blood pressure, and have not had surgery 6 months prior to plastic surgery. Recent surgeries are a risk factor for venous thromboembolism.
Are Liposuction Results Permanent
Liposuction is growing in popularity because of social media exposure and the growing acceptance of cosmetic procedures. The short downtime and low risk for infection are added bonuses for patients. In addition, once the fat is suctioned, it is unlikely it will reoccur in the same place. Fat cell removal is permanent.
To Sum it All Up
As mentioned earlier, liposuction is one of the safest cosmetic procedures. In the right environment, with a qualified plastic surgeon, and the appropriate patient complications are rare. As the number of plastic surgeons grows, increasing the competition for patients, the price of liposuction and other plastic surgery procedures is becoming affordable and accessible to more patients. CLICK HERE to see the average plastic surgeon’s fees in 2020, according to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS), 2020 Plastic Surgery Statistics. For questions about any items in this article, please consult your doctor.






